Scientists have developed a device that can translate thoughts about speech into in real time.
Although it’s still experimental, they hope the could someday help give voice to those unable to speak.
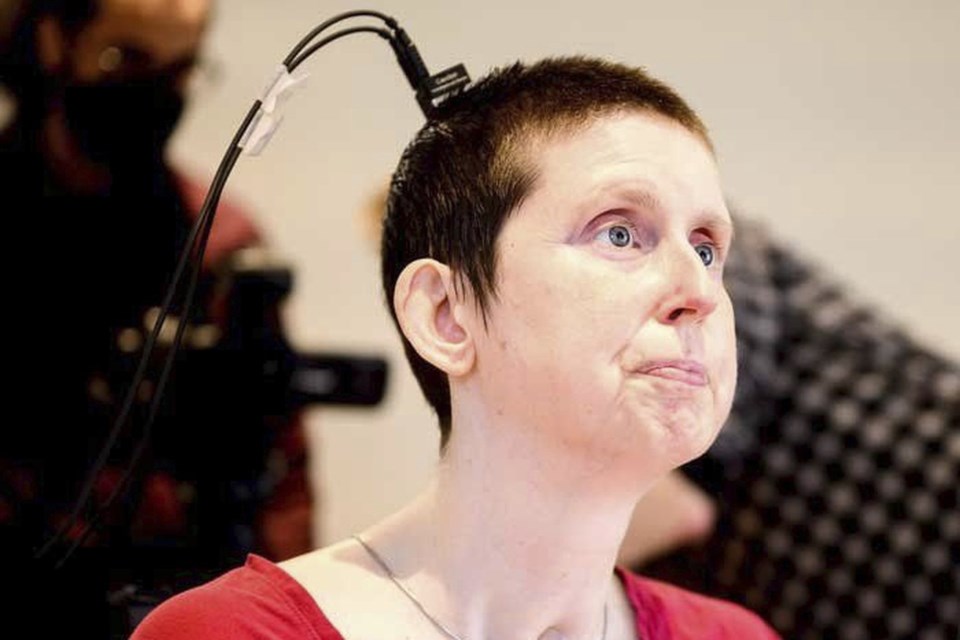
A new study described testing the device on a 47-year-old woman with quadriplegia who couldn’t speak for 18 years . Doctors implanted it in her brain during surgery as part of a clinical trial.
It “converts her intent to speak into fluent sentences,” said Gopala Anumanchipalli, a co-author of the study published Monday in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
Other brain-computer interfaces, or С����ƵIs, for speech typically have a slight delay between thoughts of sentences and computerized verbalization. Such delays can disrupt the natural flow of conversation, potentially leading to miscommunication and frustration, researchers said.
This is "a pretty big advance in our field,” said Jonathan Brumberg of the Speech and Applied Neuroscience Lab at the University of Kansas, who was not part of the study.
A team in California recorded the woman’s brain activity using electrodes while she spoke sentences silently in her brain. The scientists used a synthesizer they built using her voice before her injury to create a speech sound that she would have spoken. They trained an AI model that translates neural activity into units of sound.
It works similarly to existing systems used to transcribe meetings or phone calls in real time, said Anumanchipalli, of the University of California, Berkeley.
The implant itself sits on the speech center of the brain so that it’s listening in, and those signals are translated to pieces of speech that make up sentences. It’s a “streaming approach,” Anumanchipalli said, with each 80-millisecond chunk of speech – about half a syllable – sent into a recorder.
“It’s not waiting for a sentence to finish,” Anumanchipalli said. “It’s processing it on the fly.”
Decoding speech that quickly has the potential to keep up with the fast pace of natural speech, said Brumberg. The use of voice samples, he added, “would be a significant advance in the naturalness of speech."
Though the work was partially funded by the National Institutes of Health, Anumanchipalli said it wasn't affected by recent . More research is needed before the technology is ready for wide use, but with “sustained investments," it could be available to patients within a decade, he said.
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Science and Educational Media Group and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
Laura Ungar, The Associated Press